justineanweiler.com – In an era where digital technologies are reshaping traditional industries, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) stand out as a groundbreaking concept that promises to redefine governance, collaboration, and collective decision-making. But what exactly is a DAO, and why is it garnering so much attention?
What is a DAO?
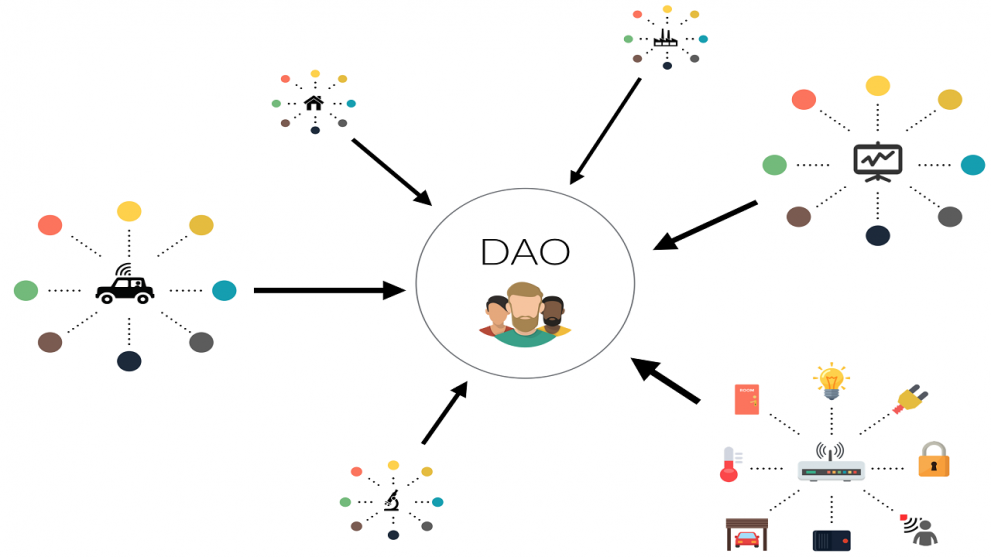
A DAO, or Decentralized Autonomous Organization, is a type of organization that operates on blockchain technology and is governed by smart contracts. Unlike traditional organizations that rely on hierarchical structures and centralized decision-making, DAOs function based on pre-defined rules encoded in smart contracts. These rules dictate how the organization operates and how decisions are made, removing the need for intermediaries and central authorities.
Key Features of DAOs
- Decentralization: Power and decision-making are distributed among members, ensuring no single entity has undue control.
- Transparency: All activities, from funding to voting, are recorded on a public blockchain, allowing members to verify and audit processes.
- Autonomy: Once launched, a DAO operates autonomously based on its code, with minimal manual intervention.
- Token-Based Governance: Members often hold tokens representing their voting power within the organization, creating a direct link between contribution and influence.
How DAOs Work
- Creation: A DAO begins with the development of smart contracts that outline its governance structure and operational rules.
- Funding: The organization raises funds through token sales, where participants buy governance tokens to become stakeholders.
- Operation: Members propose and vote on initiatives. The rules encoded in the smart contracts execute approved proposals automatically.
- Evolution: DAOs are designed to adapt through continuous member participation and updates to governance rules.
Applications of DAOs
DAOs have a wide range of use cases across industries:
- Investment Collectives: Platforms like VentureDAOs pool resources from members to invest in startups or projects.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DAOs manage lending, staking, and other financial services without intermediaries.
- Creator Economies: Artists and content creators use DAOs to distribute revenue and make collective decisions.
- Social Causes: DAOs fund and coordinate initiatives for environmental sustainability, education, and more.
Benefits of DAOs
- Efficiency: Automated processes reduce bureaucracy and speed up decision-making.
- Inclusivity: Anyone with access to the internet can participate, breaking down geographical and financial barriers.
- Accountability: Transparent operations and public records ensure accountability for all members.
Challenges Facing DAOs
While DAOs have immense potential, they also face significant challenges:
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear legal frameworks makes it difficult for DAOs to operate in compliance with existing laws.
- Security Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contracts can be exploited, leading to financial losses.
- Coordination Complexity: Achieving consensus among a large, diverse group of participants can be difficult.
- Scalability: Managing large-scale DAOs while maintaining decentralization and efficiency is a complex task.
The Future of DAOs
DAOs represent a paradigm shift in how organizations are structured and operated. As blockchain technology matures and regulatory clarity improves, DAOs are likely to play a significant role in sectors ranging from finance to philanthropy. By enabling collective decision-making and empowering communities, DAOs are set to democratize governance and foster innovation in unprecedented ways.
In conclusion, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are not just a technological innovation but a societal one. They challenge conventional notions of control, trust, and collaboration, offering a glimpse into a more decentralized and equitable future.