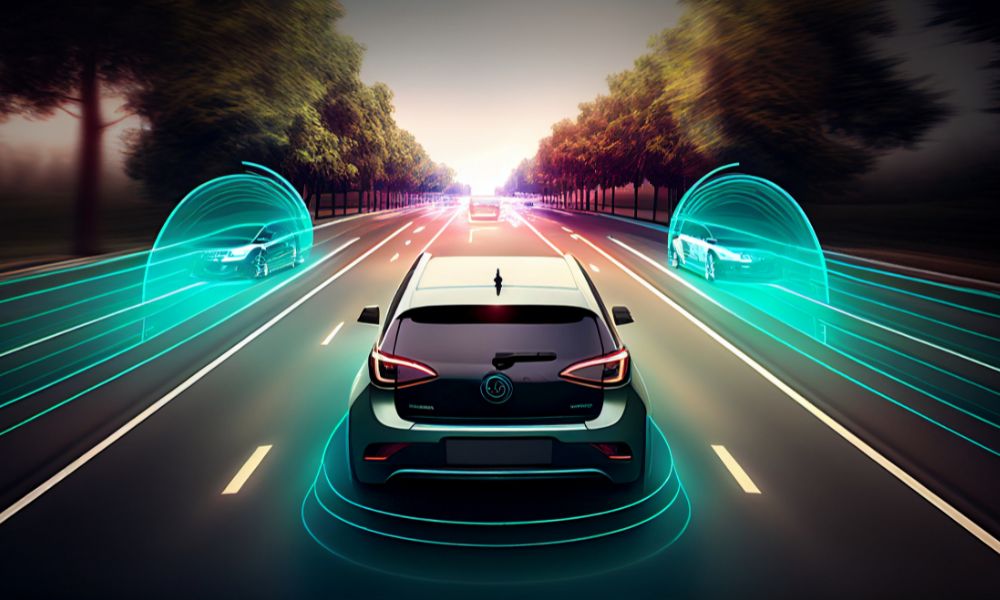
justineanweiler.com – Autonomous driving technology represents one of the most transformative advancements in transportation. With the potential to reshape urban mobility, reduce accidents, and enhance efficiency, self-driving cars are at the forefront of technological innovation. This article explores the core technologies that enable autonomous driving, the challenges faced, and the future of this exciting field.
Core Technologies
1. Sensors
At the heart of autonomous vehicles are a variety of sensors that provide critical information about the vehicle’s surroundings. These include:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser beams to create a 3D map of the environment, identifying objects and measuring distances with high precision.
- Radar: Utilized for detecting the speed and distance of nearby vehicles, radar can function in adverse weather conditions, making it essential for safe navigation.
- Cameras: High-resolution cameras capture visual data, enabling object recognition, lane detection, and traffic sign identification. Advanced image processing algorithms interpret this visual information.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Commonly used for parking assistance, these sensors detect objects in close proximity to the vehicle.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms process the vast amount of data collected from sensors. They enable vehicles to:
- Perceive the Environment: AI systems interpret sensor data to identify and classify objects, such as pedestrians, cyclists, and other vehicles.
- Make Decisions: Machine learning algorithms analyze real-time data to make driving decisions, such as when to stop, accelerate, or change lanes.
- Improve Over Time: With every mile driven, AI systems can learn from experiences, refining their decision-making processes and improving safety and efficiency.
3. Mapping and Localization
For autonomous vehicles to navigate accurately, they rely on detailed maps and precise localization systems:
- High-Definition Maps: These maps provide intricate details about roadways, including lane configurations, traffic signals, and obstacles. They are continually updated to reflect changes in the environment.
- GPS and Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): GPS provides broad location data, while IMUs offer fine-grained movement information. Together, they help vehicles understand their exact position on the map.
4. Control Systems
Control systems ensure that the vehicle responds appropriately to its environment. These systems manage:
- Steering, Acceleration, and Braking: Sophisticated algorithms govern vehicle dynamics, allowing for smooth and safe operation.
- Path Planning: Algorithms calculate the best route for the vehicle to follow, considering traffic conditions, obstacles, and intended destinations.
Challenges in Autonomous Driving
Despite significant advancements, several challenges remain in the development of autonomous driving technology:
1. Safety and Reliability
Ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles is paramount. Developers must address potential failures in hardware and software, and rigorous testing is essential to build public trust.
2. Regulatory and Legal Issues
The regulatory landscape for autonomous vehicles is still evolving. Governments must establish clear guidelines for testing, liability, and insurance in the event of accidents involving self-driving cars.
3. Ethical Considerations
As autonomous vehicles make decisions, ethical dilemmas arise. For example, how should a vehicle prioritize the safety of its passengers versus pedestrians in a potential accident scenario?
4. Public Acceptance
Public perception plays a crucial role in the adoption of autonomous driving technology. Many people are wary of self-driving cars, necessitating educational efforts to address concerns and misconceptions.
The Future of Autonomous Driving
The future of autonomous driving looks promising, with continued investment and research pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. Key trends include:
- Integration with Smart Cities: Autonomous vehicles will likely become integral to smart city infrastructure, communicating with traffic lights and other systems to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Expansion of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS): As self-driving technology matures, we may see a shift toward shared mobility solutions, reducing the need for personal vehicle ownership.
- Advancements in AI: Ongoing developments in artificial intelligence will further enhance the capabilities of autonomous vehicles, making them safer and more efficient.
Conclusion
Autonomous driving technology holds the potential to revolutionize how we think about transportation. By leveraging advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and intricate mapping systems, self-driving cars are set to change the landscape of mobility. As challenges are addressed and technology continues to evolve, the vision of a world with safe, efficient, and accessible autonomous vehicles may soon become a reality.