justineanweiler.com – The motherboard is one of the most critical components of a computer. Often referred to as the “heart” of the system, it serves as the primary circuit board that connects all hardware components, enabling them to work together harmoniously. Understanding its purpose, structure, and types is essential for anyone interested in computing.
What is a Motherboard?
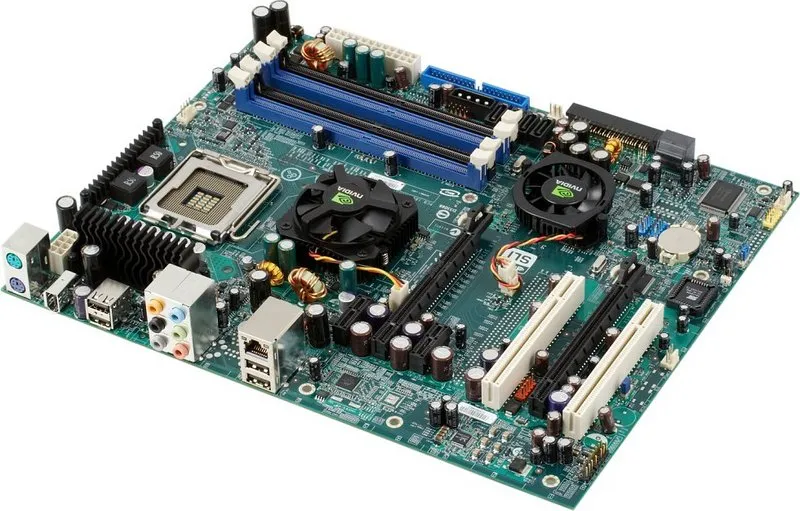
A motherboard, also known as a mainboard or system board, is a large printed circuit board (PCB) that hosts the CPU, memory, storage devices, power connectors, and peripheral devices. It provides the electrical pathways for communication between these components and ensures they operate efficiently.
Key Components of a Motherboard
- Processor Socket
The CPU socket is where the processor is installed. Different sockets are designed to support specific CPU models, such as Intel’s LGA or AMD’s AM series. - RAM Slots
These slots hold the system’s memory modules (RAM). Motherboards can vary in the number and type of RAM slots, such as DDR4 or DDR5. - Chipset
The chipset determines the motherboard’s functionality, including how data flows between the CPU, memory, and peripherals. Chipsets are divided into two parts:- Northbridge: Manages high-speed communication.
- Southbridge: Handles slower peripheral devices.
- Expansion Slots
Slots like PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) allow for the addition of GPUs, sound cards, and other expansion cards. - Storage Connectors
SATA and M.2 slots connect hard drives and SSDs. M.2 slots, in particular, support high-speed NVMe drives for faster data transfer. - Power Connectors
These supply power to the motherboard and its components, typically via 24-pin ATX and 4/8-pin CPU connectors. - I/O Ports
Integrated ports include USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and audio jacks, providing connectivity to peripherals and networks. - BIOS/UEFI Firmware
The BIOS or UEFI firmware is a small memory chip that initializes hardware during boot-up and provides system management settings.
Types of Motherboards
Motherboards come in various form factors, which determine their size, layout, and compatibility:
- ATX: Standard size for desktops, offering multiple expansion slots and ports.
- Micro-ATX: Smaller than ATX but retains functionality for budget builds.
- Mini-ITX: Compact size, ideal for small-form-factor PCs.
- E-ATX: Extended version of ATX for high-performance and gaming rigs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Motherboard
- Compatibility
Ensure the motherboard supports your CPU, RAM type, and GPU. - Expansion Needs
Consider the number of PCIe slots, USB ports, and storage connectors for future upgrades. - Build Quality
High-quality capacitors and durable PCBs ensure longevity and stable performance. - Features
Integrated features like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and RGB lighting can enhance usability and aesthetics. - Price
Motherboards range from budget-friendly options to premium models for enthusiasts and gamers.
Conclusion
The motherboard is a vital component that dictates the performance and capabilities of a computer. Choosing the right one ensures seamless communication between hardware components and provides a solid foundation for future upgrades. Whether you’re building a gaming rig, a workstation, or a budget PC, understanding motherboard specifications is key to creating a balanced and efficient system.