justineanweiler.com – In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, computing stands at the forefront of innovation. While classical computing has driven progress for decades, the emergence of quantum computing introduces a paradigm shift with unprecedented possibilities. This article explores the key differences between quantum and classical computing, their respective advantages, and how they might shape the future of technology.
Understanding Classical Computing
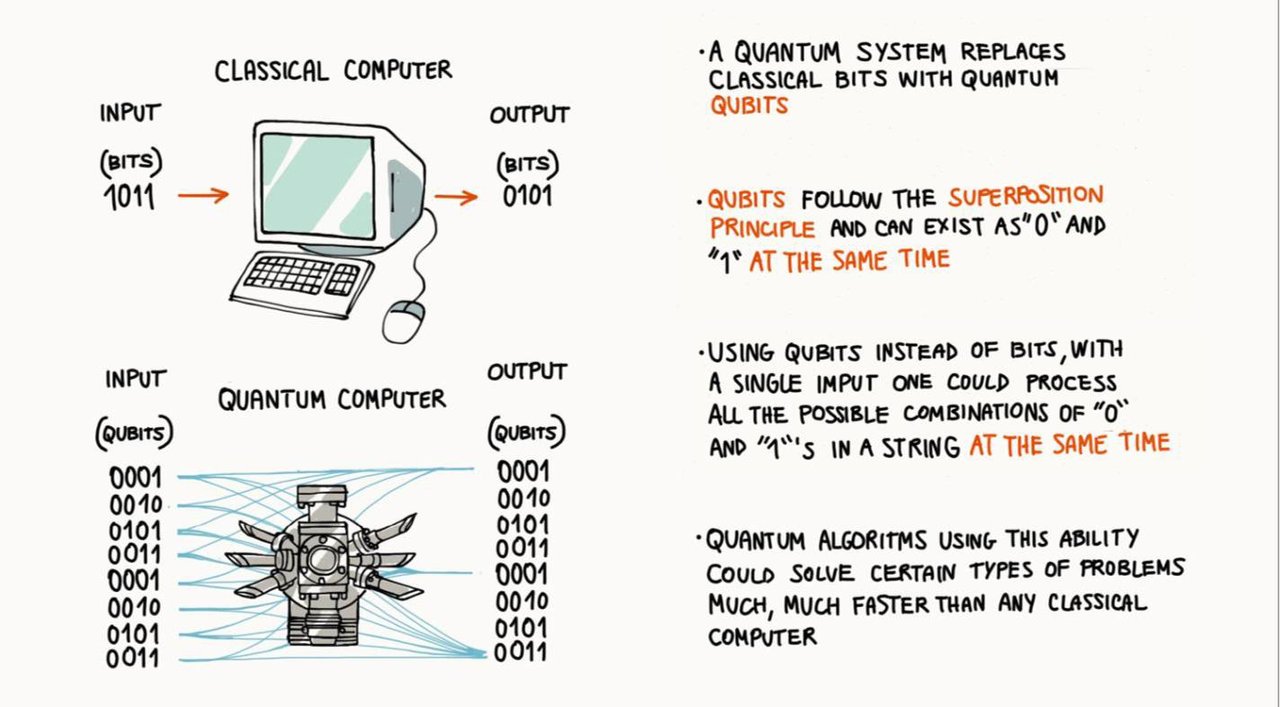
Classical computers, the devices we use daily, operate based on binary logic. They process data in the form of bits, which exist as either 0s or 1s. Using transistors, logic gates, and algorithms, classical computing performs complex calculations at incredible speeds, enabling advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and cloud computing.
The Power of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing, on the other hand, is based on the principles of quantum mechanics. Instead of using bits, quantum computers leverage qubits, which can exist in a state of 0, 1, or both simultaneously due to a phenomenon called superposition. Additionally, qubits exhibit entanglement, allowing them to be interconnected regardless of distance, leading to exponential processing power.
Key Differences
- Processing Power: Quantum computers can solve certain complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. For instance, a task that would take thousands of years for a supercomputer could be solved in minutes using a quantum system.
- Data Storage and Processing: Classical computers process one operation at a time per bit, whereas quantum computers can process multiple states simultaneously due to superposition.
- Error Rates: Classical computing is highly reliable, while quantum computers are still prone to errors due to quantum decoherence and noise, requiring significant error correction advancements.
- Application Areas: While classical computing excels in everyday tasks, gaming, and traditional software applications, quantum computing is expected to revolutionize cryptography, material science, drug discovery, and optimization problems.
The Future of Computing
Despite its enormous potential, quantum computing is still in its infancy. Researchers and tech giants like Google, IBM, and Microsoft are making strides in developing stable quantum systems. However, classical computing is far from obsolete—hybrid models combining both quantum and classical technologies are likely to be the bridge to future advancements.
As quantum computing continues to evolve, industries must prepare for a new era of computational capabilities. Whether it’s breaking encryption, optimizing logistics, or discovering new drugs, the fusion of classical and quantum computing promises an exciting future where the impossible becomes possible.
Conclusion
While classical computing remains the foundation of modern technology, quantum computing introduces an entirely new way of processing information. As research progresses, the integration of these two computing paradigms may redefine industries, scientific discoveries, and problem-solving approaches. The future of technology is not just about speed but about harnessing the power of the quantum realm to unlock new frontiers.